
Relationship between areabased leaf N (Narea) and A, gs, Vc,max,... Download Scientific Diagram
Find the perfect based on leaf forms and spaces stock photo, image, vector, illustration or 360 image. Available for both RF and RM licensing.

Leaf Forms Stock Image C017/3525 Science Photo Library
Some examples illustrating the variety of leaves. (a) The deciduous broad leaf of Liriodendron tulipifera (tulip tree) (leaf length typically about 12-15 cm).(b) The small evergreen leaves of Buxus sempervirens (boxwood).These leaves are much smaller, with lengths of 1.5-3 cm and are thicker and leathery, as is typical for leaves with a life span of 12 months and more.

Why Do Leaves Have Such Different Shapes? Leaf collage, Leaf projects, Plants
Leaf Form. Leaves may be simple or compound (Figure 30.23). In a simple leaf, the blade is either completely undivided—as in the banana leaf—or it has lobes, but the separation does not reach the midrib, as in the maple leaf.. sub-stomatal air space in the leaf. (credit: modification of work by Robert R. Wise; part c scale-bar data from.
The Role of WOX Genes in Shaping Leaf Blade Form (A) Conceptual model... Download Scientific
Based on Leaf Forms and Spaces #ARTI401410. Ask a question. Total Price: $99.00. Painting Price: $99.00 Frame Price: $0.00. Select Size Gallery Price Artisoo Price. Custom Size Order is Easy: 1. Select the size that is the closest to your required size from the size & pricing list. 2. Enter your required size into the comment box at checkout.
Optimalitybased leaf trait mapping Lab Prentice
Based on Leaf Forms and Spaces Arthur Dove Date: 1912 Style: Abstract Art Genre: figurative Order Oil Painting reproduction Tags: Flower Plant Arthur Dove Famous works Nature Symbolized • 1911 Portrait of Ralph Dusenberry • 1924 Sunrise • 1924 Foghorns • 1929 Lake Afternoon • 1935 Red Sun • 1935 Indian Summer • 1941 View all 24 artworks

Leaf Arrangement that is Parallel and Forms a Pattern. Stock Photo Image of wallpaper, vibrant
primary function of the leaf is to absorb and process sunlight and car- habitat by evolving bon dioxide for photosynthesis, few leaf structural structural features of leaves have been related mechanistically to these tasks. properties in concert For example, it has been known for over a century that the internal with leaf orientational anatomy o.

Developing polymer compositebased leaf spring systems for automotive industry
Leaf Form. There are two basic forms of leaves that can be described considering the way the blade (or lamina) is divided. Leaves may be simple or compound. Figure 35.5.2.1 35.5.2. 1: Simple and compound leaves: Leaves may be simple or compound. In simple leaves, the lamina is continuous. (a) The banana plant ( Musa sp.) has simple leaves.

LP141 Violet Leaf Forms (Set of 4)
How do leaf air spaces form? In plants, air spaces can form by cell separation or cell death. Air space formation by cell death is known as lysogeny [] and predominantly happens in roots in response to waterlogging, although in some species it also happens in stems and leaves (reviewed in [11,12]).Leaf air spaces largely form via cell separation [], which can be divided into 2 types.

Whole Group Leaf Investigation Fall kindergarten, Fall preschool, Fall lesson plans
The close tie between leaf form and function is an area of high current activity (Leishman et al., 2007), again with a focus on leaf structure, but also in terms of functional components - leaf photosynthesis, nitrogen and phosphorus. When applied to invasive plants, the approach clearly identified that exotic invasive species modified function to enable faster growth than native invasive.

Relationships between specific leaf area (leaf area per unit mass) and... Download Scientific
Abstract Understanding what controls global leaf type variation in trees is crucial for comprehending their role in terrestrial ecosystems, including carbon, water and nutrient dynamics.
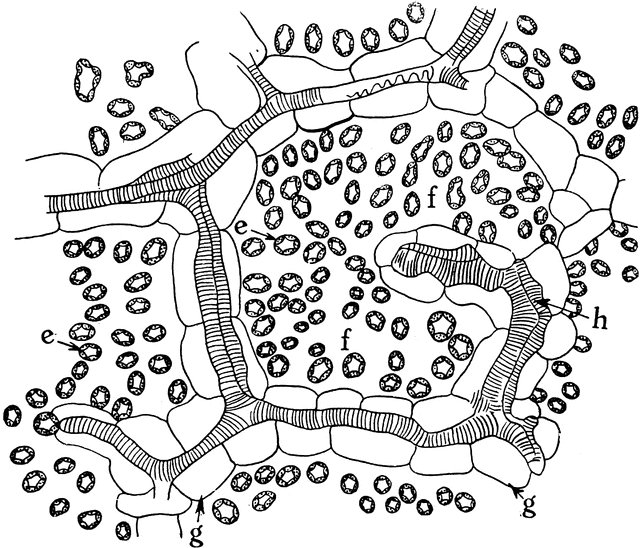
Intercellular Spaces of Leaf ClipArt ETC
Leaves are composed of interconnected functional elements that evolved in concert under high selective pressure, directed toward strategies for improving productivity with limited resources. In this paper, selected basic components of the leaf are described together with biomimetic examples derived from them.

Emma Foster CGA&A Flower, Tree & Leaf Forms
To do this, we created an allometric space for Arabidopsis mutants based on a subset of the data (five leaves from each mutant). We then used the classifications A1-D1 to define 15 regions within this allometric space.. Ponce, M R, and Micol, J L (1999). " Genetic analysis of leaf form mutants from the Arabidopsis Information Service.

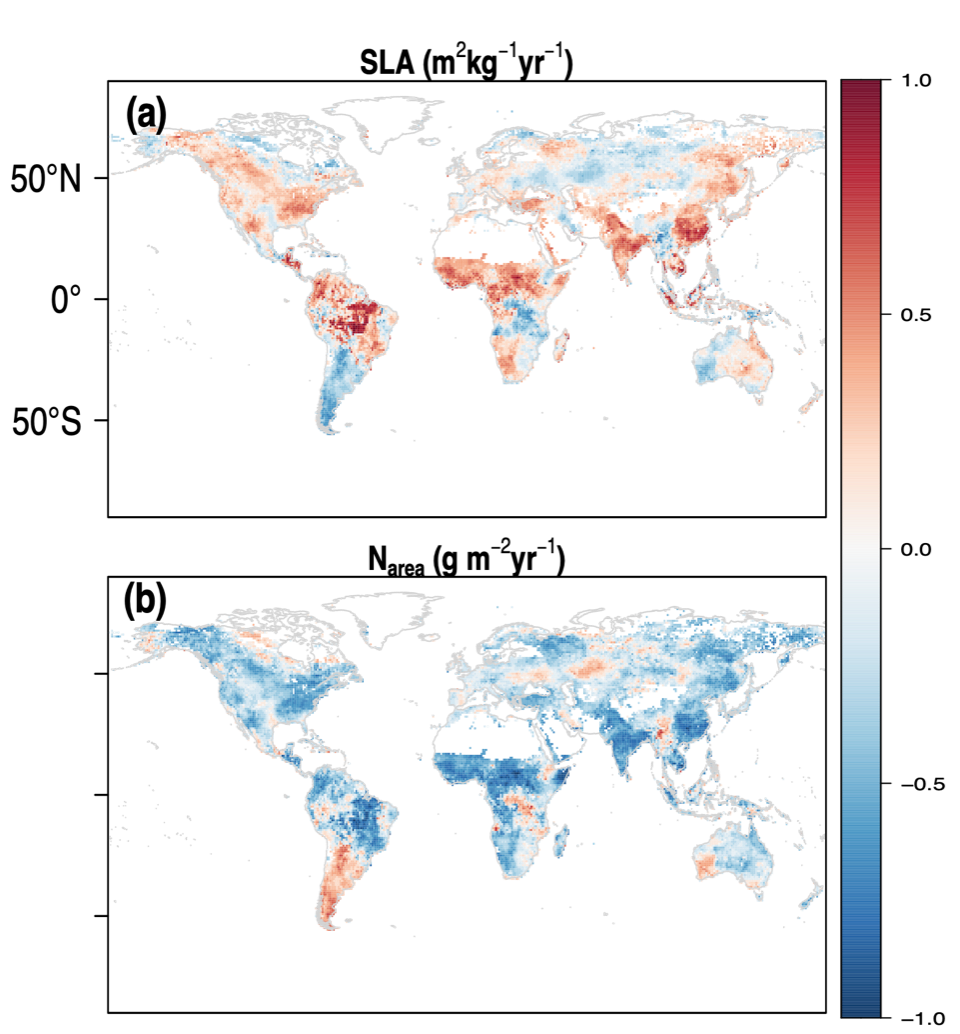
Relationships between areabased leaf photosynthetic traits and soil... Download Scientific
Figure 2: The global spectrum of plant form and function. a, Projection of global vascular plant species (dots) on the plane defined by principal component axes (PC) 1 and 2 (details in Extended.

Arthur Dove, 191112, Based on Leaf Forms and Spaces, pastel on unidentified support. Now lost
Here we provide the 'Global Spectrum of Plant Form and Function Dataset', containing species mean values for six vascular plant traits. Together, these traits -plant height, stem specific.

Figure 1 from A common developmental program can produce diverse leaf shapes Semantic Scholar
There are two basic forms of leaves that can be described considering the way the blade (or lamina) is divided. Leaves may be simple or compound. Figure 30.9.1 30.9. 1: Simple and compound leaves: Leaves may be simple or compound. In simple leaves, the lamina is continuous. (a) The banana plant ( Musa sp.) has simple leaves.

Table 2 from Deep LearningBased Leaf Disease Detection in Crops Using Images for Agricultural
The air space found between the spongy parenchyma cells allows gaseous exchange between the leaf and the outside atmosphere through the stomata. In aquatic plants, the intercellular spaces in the spongy parenchyma help the leaf float. Both layers of the mesophyll contain many chloroplasts. Figure 30.10. 1: Mesophyll: (a) (top) The central.